RapidEye image processing for soil use mapping in rugged landscape accuracy
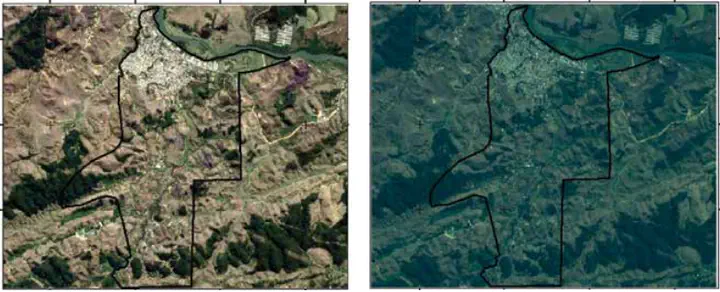 Image credit: Elias
Image credit: Elias
Resumo
The objective of this work was to analyse RapidEye satellite image characteristics, as well as to assess its orthorectification geometric accuracy and its application for land use mapping, in a rugged landscape. An atmospheric correction was applied to the images, which was followed by the assessment of the following aspects; spectral response to different targets in the uncorrected and corrected images; accuracy of the orthorectified image; and accuracy of the supervised classification. The atmospheric correction allowed a better evaluation of the spectral response of the targets. The geometrical evaluation according to the Map Accuracy Standards, classified the orthorectified image in class C at the 1:20,000 scale. The supervised classification consistently quantified the areas and the percentage of each soil use class. The distribution of classes highlights the historical effect of the use on land degradation.
Supplementary notes can be added here, including code, math, and images.